-
发表于 2024.09.10
-
一开始的做法是先用哈希表记录每一行/每一列最后一次被修改的值以及修改”时间”(即操作的序号),然后遍历矩阵,对于每一个元素,判断它的最终值来源于最后一次的行修改还是列修改,然后累加即可。这个做法的时间复杂度是
O(n^2),会超时。但是,我们可以逆向思维,从最后一次操作开始,逐步向前。如果某一行/列在后面被修改了(可使用哈希表记录),就不再处理;否则,属于该行/列的最后一次修改,其影响的元素数目是
n - 已经被修改的列/行数目。举个例子,如果当前处理某一行,此时已经有k列被修改了,那么这一行修改最终影响的元素数目就是n - k。这个做法的时间复杂度是O(n)。以LeetCode官方示例
n = 3, queries = [[0,0,4],[0,1,2],[1,0,1],[0,2,3],[1,2,1]]为例: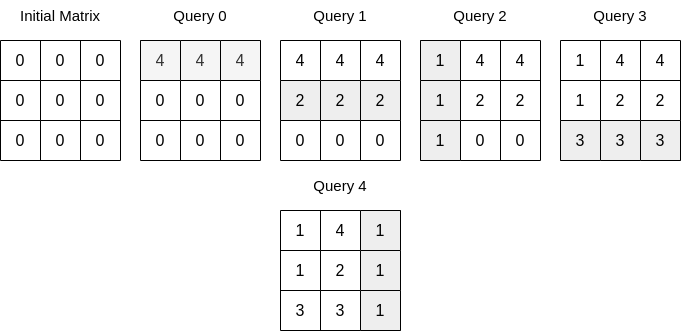
-
倒数第一次操作是
[1,2,1],即第2列被修改为1,那么第2列的最后一次修改最终影响的元素数目是3 - 0 = 3;此时,ans = ans + 1 * 3 = 3; -
倒数第二次操作是
[0,2,3],即第2行被修改为3,那么第2行的最后一次修改最终影响的元素数目是3 - 1 = 2;此时,ans = ans + 3 * 2 = 9; -
倒数第三次操作是
[1,0,1],即第0列被修改为1,那么第0列的最后一次修改最终影响的元素数目是3 - 1 = 2;此时,ans = ans + 1 * 2 = 11; -
倒数第四次操作是
[0,1,2],即第1行被修改为2,那么第1行的最后一次修改最终影响的元素数目是3 - 2 = 1;此时,ans = ans + 2 * 1 = 13; -
倒数第五次操作是
[0,0,4],即第0行被修改为4,那么第0行的最后一次修改最终影响的元素数目是3 - 2 = 1;此时,ans = ans + 4 * 1 = 17。
所以,最终的答案是
17。class Solution { public: using LL = long long; LL matrixSumQueries(int n, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { unordered_set<int> row_used, col_used; LL ans = 0; int type, index, val; for (int i = queries.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { const auto& query = queries[i]; type = query[0]; index = query[1]; val = query[2]; if (type == 0 && !row_used.count(index)) { ans += val * (n - col_used.size()); row_used.insert(index); } else if (type == 1 && !col_used.count(index)) { ans += val * (n - row_used.size()); col_used.insert(index); } if (row_used.size() == n && col_used.size() == n) break; } return ans; } };Python的做法
class Solution: def matrixSumQueries(self, n: int, queries: List[List[int]]) -> int: ans = 0 row_used = set() col_used = set() for type_, index, val in reversed(queries): if type_ == 0 and index not in row_used: row_used.add(index) ans += val * (n - len(col_used)) elif type_ == 1 and index not in col_used: col_used.add(index) ans += val * (n - len(row_used)) if len(row_used) == n and len(col_used) == n: break return ans超时的版本:
class Solution: def matrixSumQueries(self, n: int, queries: List[List[int]]) -> int: row_info = {} col_info = {} for t, (type_, index, val) in enumerate(queries): if type_ == 0: row_info[index] = (t, val) else: col_info[index] = (t, val) ans = 0 for i in range(n): for j in range(n): rt, rval = row_info.get(i, (-1, 0)) ct, cval = col_info.get(j, (-1, 0)) val = rval if rt > ct else cval ans += val return ans -
- LC 题目链接
-